Pipelines for merge requests (FREE)
Introduced in GitLab 11.6.
In a basic configuration, GitLab runs a pipeline each time changes are pushed to a branch.
If you want the pipeline to run jobs only on commits associated with a merge request, you can use pipelines for merge requests.
These pipelines are labeled as detached in the UI, and they do not have access to protected variables.
Otherwise, these pipelines are the same as other pipelines.
Pipelines for merge requests can run when you:
- Create a new merge request.
- Commit changes to the source branch for the merge request.
- Select the Run pipeline button from the Pipelines tab in the merge request.
If you use this feature with merge when pipeline succeeds, pipelines for merge requests take precedence over other pipelines.
Prerequisites
To enable pipelines for merge requests:
- Your repository must be a GitLab repository, not an external repository.
- You must have the Developer role to run a pipeline for merge requests.
Configure pipelines for merge requests
To configure pipelines for merge requests, you must configure your CI/CD configuration file.
To do this, you can use rules or only/except.
Use rules to run pipelines for merge requests
GitLab recommends that you use the rules keyword, which is available in
workflow:rules templates.
Use only or except to run pipelines for merge requests
You can use the only/except keywords. However, with this method, you must specify only: - merge_requests for each job.
In the following example, the pipeline contains a test job that is configured to run on merge requests.
The build and deploy jobs don't have the only: - merge_requests keyword,
so they don't run on merge requests.
build:
stage: build
script: ./build
only:
- main
test:
stage: test
script: ./test
only:
- merge_requests
deploy:
stage: deploy
script: ./deploy
only:
- mainExclude specific jobs
When you use only: [merge_requests], only jobs with
that keyword are run in the context of a merge request. No other jobs run.
However, you can invert this behavior and have all of your jobs run except
for one or two. For example, you might have a pipeline with jobs A, B, and C, and you want:
- All pipelines to always run
AandB. -
Cto run only for merge requests.
To achieve this outcome, configure your .gitlab-ci.yml file as follows:
.only-default: &only-default
only:
- main
- merge_requests
- tags
A:
<<: *only-default
script:
- ...
B:
<<: *only-default
script:
- ...
C:
script:
- ...
only:
- merge_requests-
AandBalways run, because they get theonly:rule to execute in all cases. -
Conly runs for merge requests. It doesn't run for any pipeline except a merge request pipeline.
In this example, you don't have to add the only: rule to all of your jobs to make
them always run. You can use this format to set up a Review App, which helps to
save resources.
Exclude specific branches
Branch refs use this format: refs/heads/my-feature-branch.
Merge request refs use this format: refs/merge-requests/:iid/head.
Because of this difference, the following configuration does not work as expected:
# Does not exclude a branch named "docs-my-fix"!
test:
only: [merge_requests]
except: [/^docs-/]Instead, use the
$CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME predefined environment
variable in
combination with
only:variables to
accomplish this behavior:
test:
only: [merge_requests]
except:
variables:
- $CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME =~ /^docs-/Run pipelines in the parent project for merge requests from a forked project (PREMIUM)
- Introduced in GitLab 13.3.
- Moved to GitLab Premium in 13.9.
By default, external contributors who work in forks can't create pipelines in the parent project. When a merge request that comes from a fork triggers a pipeline:
- The pipeline is created and runs in the fork (source) project, not the parent (target) project.
- The pipeline uses the fork project's CI/CD configuration and resources.
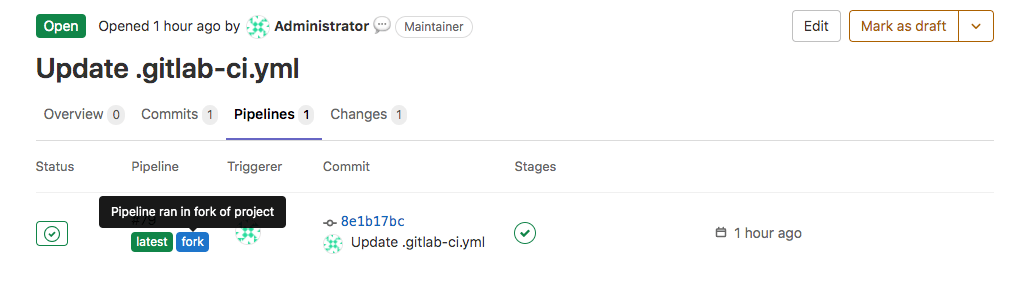
If a pipeline runs in a fork, a fork badge appears for the pipeline in the merge request.
Sometimes parent project members want the pipeline to run in the parent project. They may want to ensure that the post-merge pipeline passes in the parent project. For example, a fork project could try to use a corrupted runner that doesn't execute test scripts properly, but reports a passed pipeline. Reviewers in the parent project could mistakenly trust the merge request because it passed a faked pipeline.
Parent project members with at least the Developer role can create pipelines in the parent project for merge requests from a forked project. In the merge request, go to the Pipelines tab and select Run pipeline.
WARNING: Fork merge requests can contain malicious code that tries to steal secrets in the parent project when the pipeline runs, even before merge. As a reviewer, you must carefully check the changes in the merge request before triggering the pipeline. GitLab shows a warning that you must accept before you can trigger the pipeline.
Predefined variables available for pipelines for merge requests
When you use pipelines for merge requests, additional predefined variables are available to the CI/CD jobs. These variables contain information from the associated merge request, so that you can integrate your job with the GitLab Merge Request API.
Troubleshooting
Two pipelines created when pushing to a merge request
If you are experiencing duplicated pipelines when using rules, take a look at
the important differences between rules and only/except,
which helps you get your starting configuration correct.
If you are seeing two pipelines when using only/except, please see the caveats
related to using only/except above (or, consider moving to rules).
In GitLab 13.7 and later,
you can add workflow:rules to switch from branch pipelines to merge request pipelines.
After a merge request is open on the branch, the pipeline switches to a merge request pipeline.
Two pipelines created when pushing an invalid CI configuration file
Pushing to a branch with an invalid CI configuration file can trigger the creation of two types of failed pipelines. One pipeline is a failed merge request pipeline, and the other is a failed branch pipeline, but both are caused by the same invalid configuration.